In simple words red teaming is an ethical hacking exercise that is done by organizations occasionally to test their defense system. It is performed by ethical hackers who mirror the conditions of a real-world attack using TTPs that is used by real adversaries.
It ensures the engagements are as authentic as possible.
However, an exercise takes weeks or months to complete.
Benefits of Red Teaming
Red Teamers are external agents hired by organizations, who come to do this exercise in the organization. Some of the benefits of this exercise are given below.
- Assessing preparedness to defend against cyber attacks
- Testing the effectiveness of security against processes and people
- Identify the security gaps
- Improve the effectiveness of the response procedure
- Address risks and mitigate vulnerabilities
- Find the road map for future security practices
The Red Team Methodology
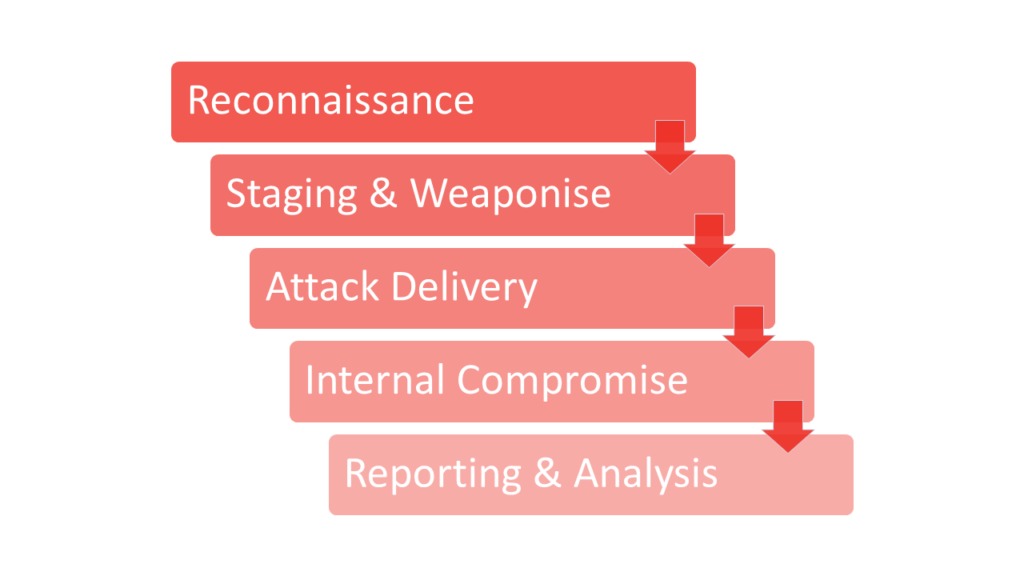
A red team exercise is conducted using the following process :
- Reconnaissance – This stage is formed with intelligence gathering. Red teamers will first survey the attack floor and understand the gaps. A good recon can stop an attack right at the initiation stage
- Staging and Weaponise – Post recon and finding vulnerabilities, the next stage is staging the attack. In this stage the red teamers can set up various hacking techniques like social engineering, phishing, using malicious codes, etc to perform the attack
- Attack Delivery – This is where red teamers will find a foothold in the client network by unleashing various weapons on targets.
- Internal Compromise – In this, the red teamers will move towards a physical compromise. Basically, once the attack is delivered, the red teamers will focus on meeting the objectives. Activities at this stage could include lateral movement across the network, privilege escalation, physical compromise, command and control activity, and data exfiltration
- Reporting and Analysis – At the end of the engagement, the red team provides a report that talks about the findings of the exercise. It lets the whole team know of the shortfalls and the security gaps.
Learnings From Red Teaming Exercise
Red teaming is a goal-based exercise unlike pentesting, it is also a stealth operation.
A red team exercise will open your eyes to the following details in your organization :
- Learning how easy it is for attackers to enter your organization security systems
- Identification of methods that could be used to disrupt business
- Expose gaps in surveillance that can be used to evade detection
- Finding out how effective is your incident response plan
Problems With Traditional Red Teaming
While red teaming is a very effective defense technique, there are few limitations that stop it from being scalable.
- A traditional red teaming is done occasionally by the organization
- Involves a big budget
- Is manual and time-consuming.
Besides doing a red teaming exercise once a year does not solve the problem that threat actors are sitting and attacking your assets every day. They need to win once whereas you as an organization need to win everyday.
The Red Team Landscape
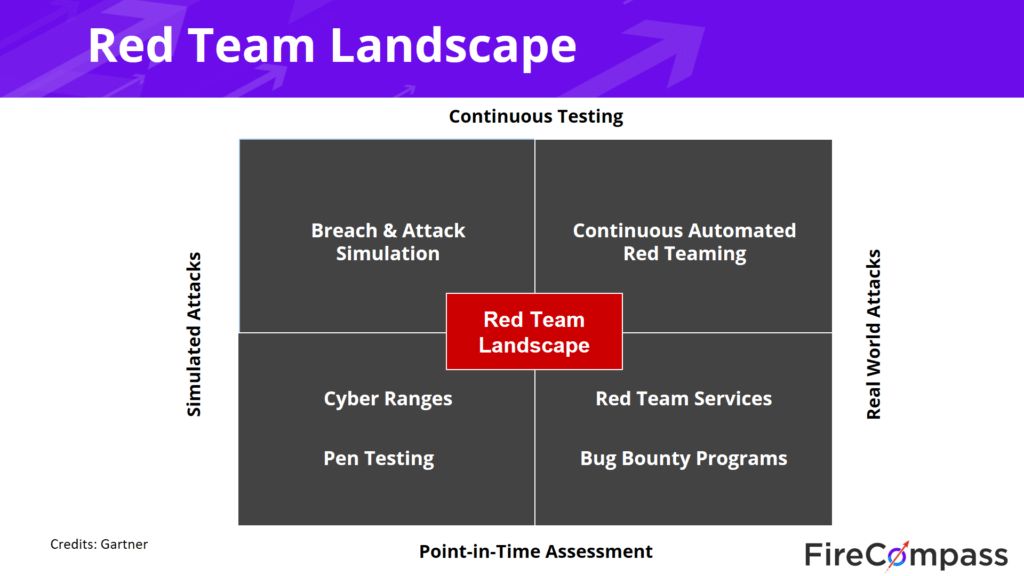
Presently there are two types of security controls; one can either make a point in time assessment or conduct continuous testing. And to protect yourself, you either have the choice of conducting simulated attacks or real-world attacks. Breach & attack simulation, and penetration testing are presently common; however, the range is limited, considering they are a point in time testing and simulated attacks.
Continuous Automated Red Teaming (CART) is an upcoming technology that fills the gap between continuous attacks and real-world attacks.
Firecompass is one of the few organizations that has recently launched a Saas based platform for CART.
Changing Nature Of Red Teaming And Emerging New Technologies - Continuous Automated Red
Teaming (CART)
Continuous Automated Red Teaming is this new emerging technology that is designed to automate red teaming so that one can achieve the breadth and depth of the process to make it scalable to conduct continuous proactive testing.
During the CART process, an organization can search already indexed deep, dark, and surface web data using similar reconnaissance techniques as threat actors. It automatically discovers an organization’s dynamic digital attack surface, including unknown exposed databases, cloud buckets, code leaks, exposed credentials, risky cloud assets, and open ports, etc.




